Sodium Laureth Sulfate (SLES) is a widely used surfactant in the personal care and cleaning product industries. Chemically known as sodium lauryl ether sulfate, SLES is an anionic detergent and surfactant found in many personal care products such as soaps, shampoos, and toothpaste, as well as in industrial cleaning agents. Its popularity stems from its excellent foaming and emulsifying properties, which are crucial for the effectiveness and consumer appeal of these products.
Structure
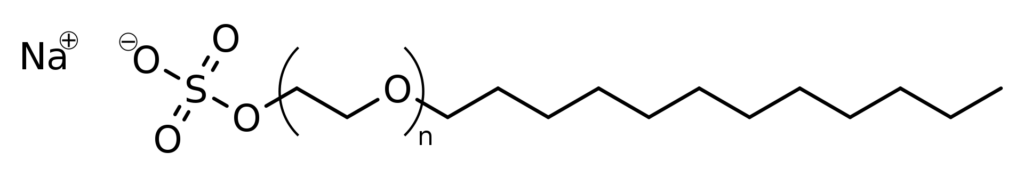
Structurally, SLES is derived from ethoxylation of dodecanol (lauryl alcohol), followed by subsequent sulfation and neutralization. The chemical structure can be summarized as CH₃(CH₂)₁₀CH₂(OCH₂CH₂)nOSO₃Na, where “n” denotes the number of ethoxy groups, typically ranging from 1 to 3 in commercial products. This molecular structure is responsible for its amphiphilic nature, meaning it has both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) properties, which enable it to effectively reduce the surface tension of water, emulsify oils, and suspend soil, making it an effective cleaning agent.
Synthesis Overview
The synthesis of SLES begins with the ethoxylation of lauryl alcohol, which involves the addition of ethylene oxide to the alcohol, forming ethoxylated lauryl alcohol. This intermediate is then treated with sulfur trioxide or chlorosulfuric acid to produce the sulfate ester, which is finally neutralized with sodium hydroxide to yield SLES. This process results in a product that is a mixture of various ethoxylated chains, contributing to its effectiveness as a surfactant.
Applications Overview
SLES is popular in the formulation of household and personal care products due to its cost-effectiveness, ability to produce rich lather, and its compatibility with a wide range of ingredients. It is a primary surfactant in many shampoos and body washes, providing the foaming action that consumers expect. In toothpaste, it helps in the removal of food particles and in maintaining oral hygiene. Additionally, SLES is used in various cleaning products, including dishwashing liquids and laundry detergents, where its ability to emulsify oils and suspend dirt is highly valued.
Global Trade Overview
On a global scale, the market for SLES is substantial, driven by the continuous demand for personal care and cleaning products. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, represents a significant portion of this market due to rapid urbanization, increasing disposable income, and rising awareness of personal hygiene. North America and Europe also hold considerable market shares, driven by the established personal care industries and a growing inclination towards premium and organic products, which still often use SLES due to its effectiveness and safety when used within recommended concentrations.
Despite its widespread use, SLES has faced scrutiny regarding its safety and environmental impact. While generally considered safe for use in cosmetics and cleaning products, concerns about skin irritation and the presence of trace impurities like 1,4-dioxane, a potential carcinogen, have led to increased regulatory oversight and demand for higher purity standards in its production. Environmentally, the biodegradability of SLES is a significant factor, and it is generally regarded as biodegradable, but the rate and extent of its degradation can vary depending on environmental conditions.
Overall, Sodium Laureth Sulfate remains a cornerstone ingredient in many formulations due to its versatile properties, economic feasibility, and efficiency. Its continued use is supported by ongoing research and development aimed at improving its safety profile and reducing its environmental footprint, ensuring that it remains a valuable component in the global market for personal care and cleaning products.



